Understanding the Basics of Regulator Circuits

by Suntop
2025-12-29
Regulator circuits are vital in electronics, ensuring devices receive stable power. They maintain a constant voltage output, protecting sensitive components.
Understanding these circuits is crucial for anyone working with electronics. They are found in power supplies, battery chargers, and many electronic devices.
Voltage regulators come in two main types: linear and switching. Each type has its own advantages and applications.
The components of a regulator circuit include resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors. These elements work together to regulate voltage levels.
This article will explore the basics of regulator circuits, their components, and their importance in electronics.
What Is a Regulator Circuit?
A regulator circuit ensures a constant voltage output despite changes in input voltage or load conditions. It is a pivotal component in electronic systems, preventing fluctuations that could damage delicate electronics.
The primary function of a voltage regulator is to deliver consistent voltage levels. This stability allows devices to function reliably and efficiently under varying conditions.
Key characteristics of regulator circuits include:
- Voltage Regulation: Maintains steady voltage output.
- Current Adjustment: Modifies current to achieve desired voltage.
- Protection: Safeguards components from voltage spikes.
In essence, regulator circuits are the guardians of electronic devices. They ensure that the device operates within its safe voltage range.
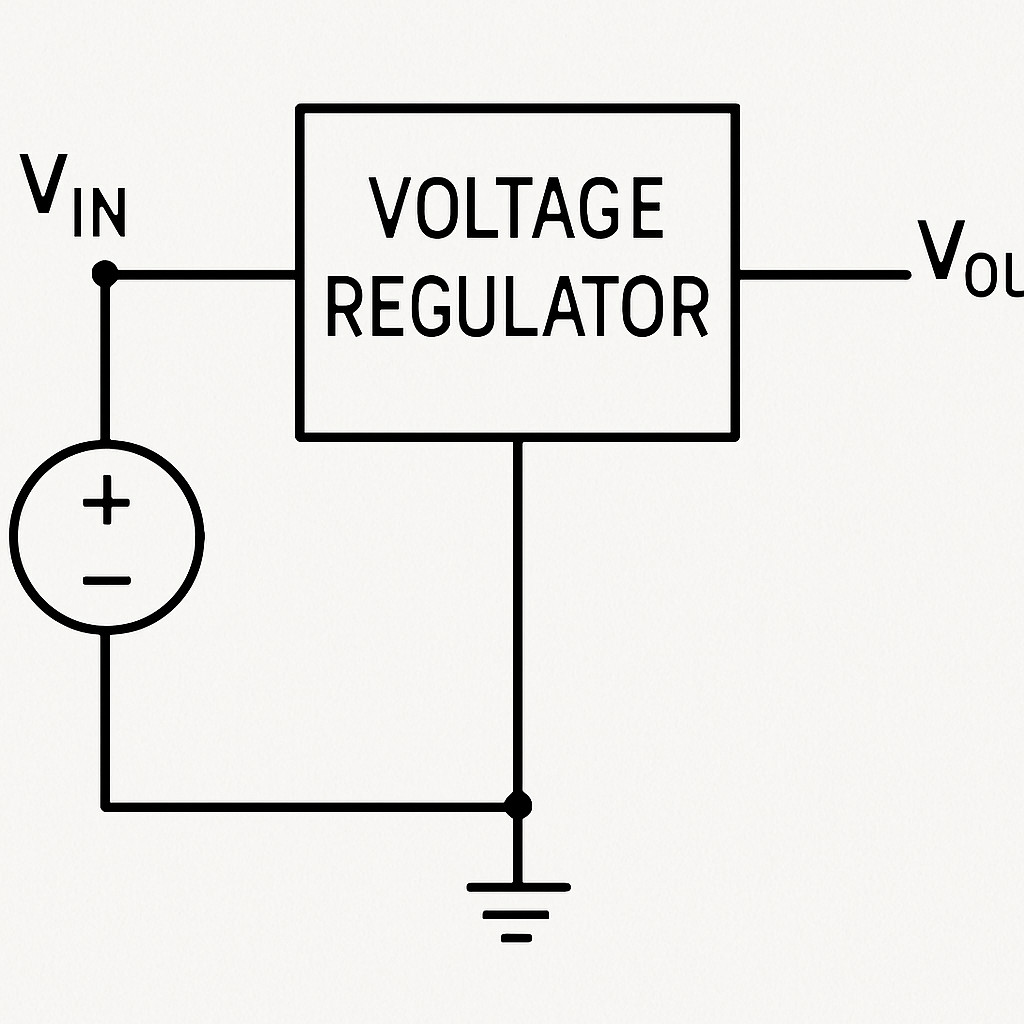
Understanding regulator circuits aids in designing and troubleshooting various electronic systems, enhancing device performance and longevity.
Why Voltage Regulation Matters in Electronics
Voltage regulation is crucial for the safety and efficiency of electronic devices. Without it, devices can suffer from instability or even damage. Overvoltage can lead to overheating, while undervoltage might cause malfunction.
Stable voltage is essential for components that require precise power levels. Variations in voltage can result in erratic performance or reduced lifespan of components. This is why voltage regulation is indispensable in electronic design.
Key benefits of voltage regulation include:
- Consistent Device Performance: Ensures devices operate smoothly.
- Component Protection: Prevents damage from voltage fluctuations.
- Extended Lifespan: Increases the durability of electronic parts.
Reliable voltage regulation is, therefore, vital to maintaining the functionality and longevity of electronic systems.
Key Components of a Voltage Regulator Circuit
A voltage regulator circuit comprises several crucial components that work together to ensure consistent voltage output. Each part plays a specific role in the regulation process, stabilizing voltage levels efficiently.
Key components include:
- Resistors: Control current flow and divide voltage.
- Capacitors: Store and release energy, smoothing voltage fluctuations.
- Diodes: Allow current to flow in one direction, providing protection.
- Transistors: Amplify or switch electronic signals, crucial for regulation.
These components collaborate to maintain the desired voltage level. The correct arrangement of these parts influences the circuit’s efficiency and performance. The specific design depends on the intended application and power requirements.
Understanding each component’s role is vital for effective circuit design. Careful selection and integration ensure reliable voltage regulation. Opting for high-quality components can markedly improve a circuit’s reliability and longevity.
Below is a basic voltage regulator schematic highlighting these components:
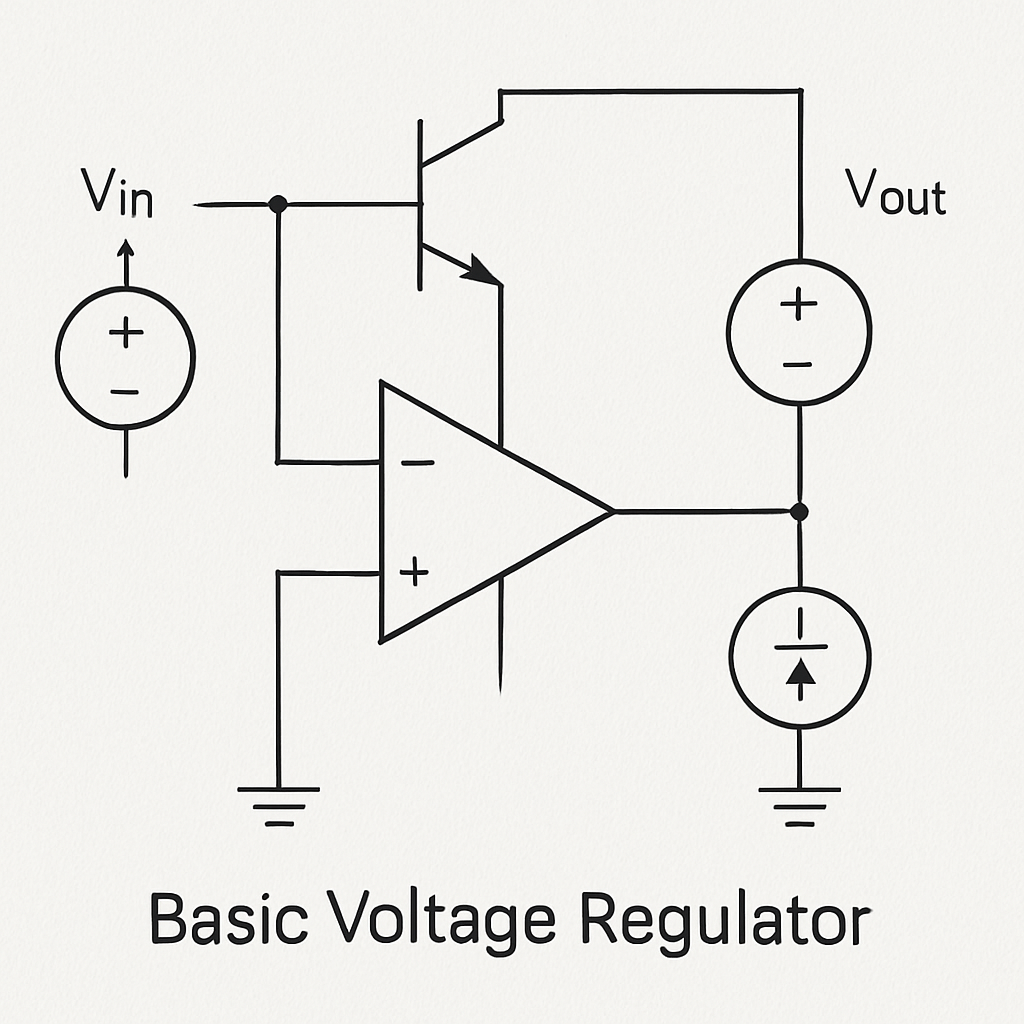
A well-designed voltage regulator circuit is key to achieving stable performance in electronic systems.
Types of Voltage Regulators: Linear vs. Switching
Voltage regulators are essential in electronics, providing stable power. They come in two primary types: linear and switching. Each serves different needs in electronic designs.
Linear voltage regulators are straightforward and low-noise. They operate efficiently within low-power applications. However, they’re less efficient in high-voltage scenarios due to energy waste as heat.
On the other hand, switching voltage regulators are versatile and efficient for high-power uses. They offer greater efficiency by transforming input power into controlled output. Despite their complexity, they suit devices needing higher power efficiency.
When choosing a regulator type, consider the specific application. Key factors include efficiency, heat generation, and complexity. While linear regulators are simpler, switching ones are more adaptable.
Below is an image illustrating both types:

Ultimately, the choice depends on the application’s requirements. Considering these aspects ensures optimal performance and efficiency.
Linear Voltage Regulators
Linear voltage regulators maintain a constant output by dissipating excess voltage as heat. They are easy to use and integrate into circuits. This simplicity makes them ideal for low-power applications and sensitive equipment.
Linear regulators provide:
- Low noise: Ensures minimal interference in signals.
- Easy design: Suits beginners and basic electronic tasks.
- Compact size: Fits into tight spaces easily.
However, their efficiency drops with high input voltages. Most linear regulators are limited by their inherent heat generation, which restricts their usage to low-power devices. Choosing the right linear regulator involves considering the trade-off between simplicity and efficiency.
For visual understanding, here’s a linear voltage regulator schematic:
Despite their limitations, linear regulators are invaluable in many traditional electronics
Switching Voltage Regulators
Switching voltage regulators excel in efficiency, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They convert input voltage to a desired level by rapidly switching elements on and off. This method conserves energy, reducing waste.
Benefits of switching regulators include:
- High efficiency: Suitable for high-power applications.
- Flexibility: Supports various voltage ranges.
- Compact cooling: Reduces the need for heat sinks.
However, they generate electrical noise, which can affect sensitive circuits. Their complex design makes them challenging for beginners. Despite this, their advantages often outweigh the disadvantages for many applications.
Here’s a schematic for better understanding:
In high-power scenarios, switching regulators offer compelling benefits despite their complexity. Their efficiency makes them indispensable in modern electronics.
How Does a Voltage Regulator Work?
Understanding how a voltage regulator works is crucial for anyone involved in electronics. A voltage regulator maintains a consistent output voltage, despite fluctuations in input voltage or load conditions. This process involves various circuit components working together harmoniously.
A voltage regulator directly controls the voltage output by adjusting the current flow. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of its operation:
- Input Signal: Voltage enters the regulator, which detects fluctuations.
- Control Mechanism: The regulator adapts to maintain steady voltage.
- Output Delivery: A stable voltage is delivered to connected devices.
Most regulators use feedback systems to monitor and adjust the voltage continuously. This mechanism ensures that the output remains within the specified limits. It’s a delicate balance between input variation and output stability.
Below is a diagram illustrating the basic operation:
By understanding these principles, one can design and optimize systems for consistent performance. This knowledge is fundamental in preventing electronic components from damage due to unstable power.
Common Voltage Regulator Circuits and Schematics
Voltage regulator circuits come in various forms, each designed for specific applications and requirements. Understanding common circuit types can significantly enhance your ability to design and troubleshoot electronic systems. These circuits provide stable voltage critical for device functionality.
One popular configuration is the series regulator circuit. It features a series transistor with a feedback system for voltage stabilization. Another common design is the shunt regulator, which diverts excess voltage away from the load to maintain stability.
Here are some typical types of voltage regulator circuits:
- Series Regulator Circuit
- Shunt Regulator Circuit
- Integrated Circuit (IC) Voltage Regulator
Each type of circuit has its strengths and limitations. The choice largely depends on the application’s requirements and constraints. For instance, integrated circuit regulators offer compactness and simplicity.
Below is a power regulator schematic example:

Here is another image showing a voltage regulator circuit diagram:
These diagrams are invaluable tools for engineers and technicians. They provide a visual representation of how components interact within the system. By understanding these schematics, you gain insights into the flow and regulation of electricity in various applications.
Voltage Regulator Calculations and Design Considerations
Designing an effective voltage regulator circuit requires careful calculations and planning. The process begins with determining the desired output voltage and current. This helps in selecting appropriate components and ensuring efficient circuit operation.
When designing, it’s crucial to consider various factors such as component ratings, heat dissipation, and efficiency. These elements influence the overall performance and reliability of the regulator circuit.
Key calculations include:
- Input Voltage Range
- Output Voltage and Current
- Power Dissipation
- Efficiency
Incorporating these calculations into the design phase ensures the circuit meets desired specifications. A detailed design boosts reliability and prolongs the life of electronic components.
Here’s an example image depicting a simplified voltage regulation calculation:

Understanding these calculations will enhance your design skills and contribute to efficient electronic systems. Proper planning is key to successful regulator circuit implementation.
Applications of Regulator Circuits in Electronics
Regulator circuits play a pivotal role across many electronics applications. These circuits ensure devices receive a stable power supply, which is vital for performance. From consumer gadgets to complex industrial systems, voltage regulators are indispensable.
Here are common applications:
- Power Supplies: Ensure consistent voltage for sensitive components.
- Battery Chargers: Maintain proper voltage levels during charging.
- Automotive Systems: Protect electronics from fluctuating vehicle power supplies.
- Telecommunications: Provide stable power in telecom equipment.
By maintaining steady voltage levels, regulator circuits help protect and enhance the longevity of electronic devices in various sectors. Their versatility makes them essential in today’s technology-driven world.
Troubleshooting and Best Practices for Regulator Circuits
Addressing issues in regulator circuits requires a systematic approach. First, check for common problems such as overheating or poor connections. Identifying faulty components can also solve many issues.
For effective troubleshooting, consider these best practices:
- Use Quality Components: Ensure long-term reliability.
- Maintain Proper Heat Dissipation: Prevent overheating.
- Regularly Inspect Connections: Avoid unexpected failures.
- Measure Input and Output Voltages: Verify consistent performance.
By adhering to these practices, you can minimize downtime and enhance the efficiency of your regulator circuits. Keeping these guidelines in mind is crucial for optimal circuit performance.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Regulator Circuits
Grasping the basics of regulator circuits enhances your electronics knowledge. It also helps in designing more reliable systems. Knowing how these circuits maintain voltage stability is invaluable.
A solid understanding aids in troubleshooting and optimizing circuit performance. This knowledge is fundamental for anyone working with electronic devices.
SUNTOP
Founded in 2000, Suntop is one of the leading global distributors of electronic components, dedica ted to providing comprehensive procurement and supply chain services to the global electronics manufacturing industry. Our services include distribution, spot trading, PPV cost-saving projects, and inventory management. We not only offer high-quality products but also strive to assist our clients in achieving optimal solutions with minimal time and cost.
Suntop is a popular choice for those seeking electron devices and circuits due to their competitive pricing and reliable service. They cater to both small-scale hobbyists and large-scale manufacturers, ensuring that every customer finds what they need.