Phase Shifters: Applications of Phase Shifters in Technology

by Suntop
2025-08-12
Phase shifters are vital components in modern technology. They adjust the phase angle of signals,enhancing system performance.
These devices are crucial in fields like telecommunications, radar, and signal processing. They help improve signal quality and reduce interference.
Phase shifters come in various types, including RF, digital, and the high-performance maestro phase shifters. Each type serves specific applications and offers unique benefits.
RF phase shifters are essential in radio frequency applications, controlling the phase of RF signals.Digital phase shifters provide precision and flexibility through digital control.
Maestro phase shifters are known for their high performance in demanding environments. They are integral to phased array antennas, enabling electronic beam steering.
In communication systems, phase shifters enhance efficiency and effectiveness. They are also used in radar systems to direct radar beams accurately.
The development of phase shifters is driven by the need for efficient, compact systems. They are key in advancing 5G technology and smart antennas.
Understanding phase shifters is crucial for engineers and technology enthusiasts. Their applications continue to expand with advancements in electronics and communication.
What is a Phase Shifter?
A phase shifter is an electronic device used to alter the phase angle of signals. It plays a crucial role in many electronic systems.
These devices are essential for controlling signal phases in various applications. By modifying the phase, they enable precise signal manipulation.
Phase shifters are found in an array of technologies, including communication and radar systems. They enhance system capabilities by improving signal alignment.
They can be implemented in different forms and materials. Each type has specific features suited to certain tasks.
To better understand their functionality, consider some core attributes:
- Phase angle adjustment: Allows signal phase changes for better alignment.
- Signal control: Facilitates accurate steering of electronic beams.
- Technology application: Integral in technologies like phased array antennas.
In practical applications, phase shifters improve efficiency and system performance by ensuring signals are in the desired phase.prove efficiency and system performance by ensuring signals are in the desired phase.
How Do Phase Shifters Work?
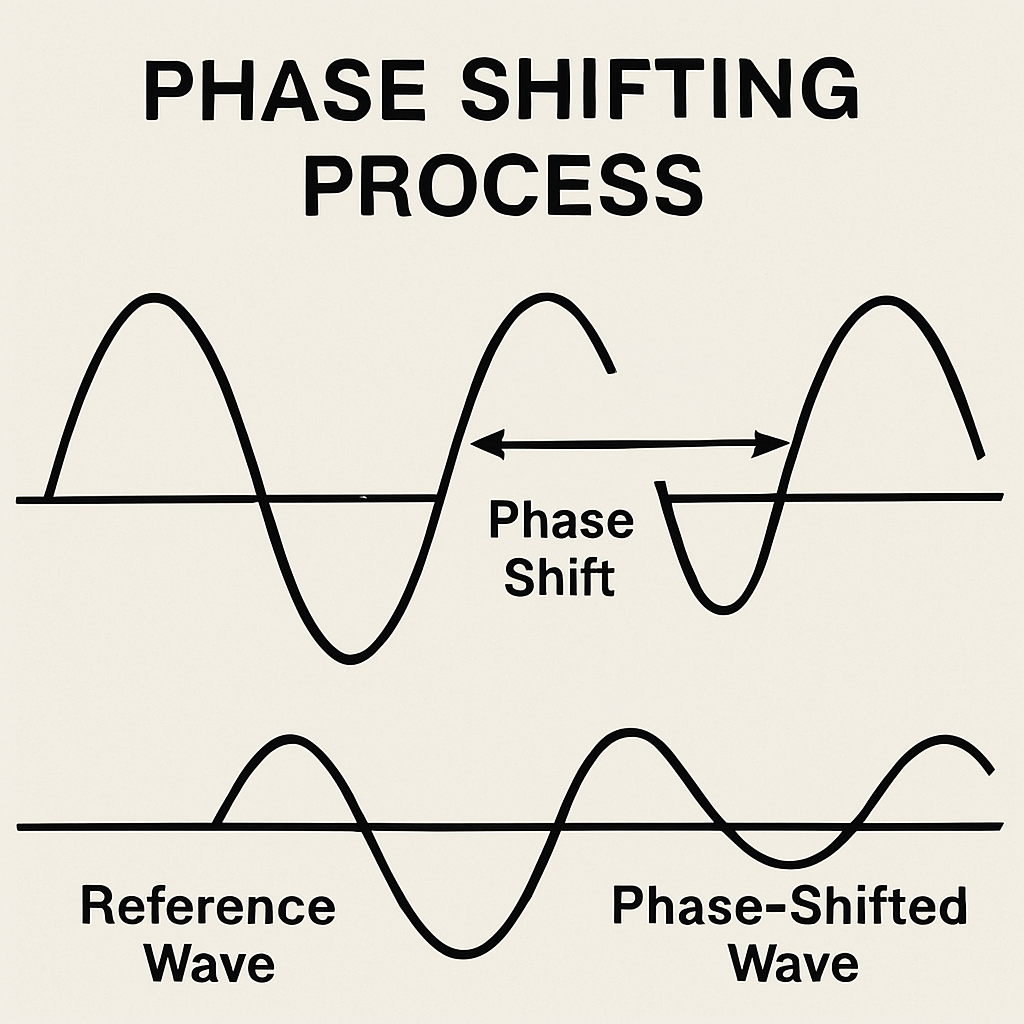
Phase shifters operate by changing the phase of an input signal. They achieve this by introducing a deliberate phase delay.
These devices can be designed using various technologies such as digital, analog, and RF circuits. Each approach has unique mechanisms.
The basic principle involves shifting the phase of the input wave without altering its frequency or amplitude. This manipulation enhances control over signal paths.
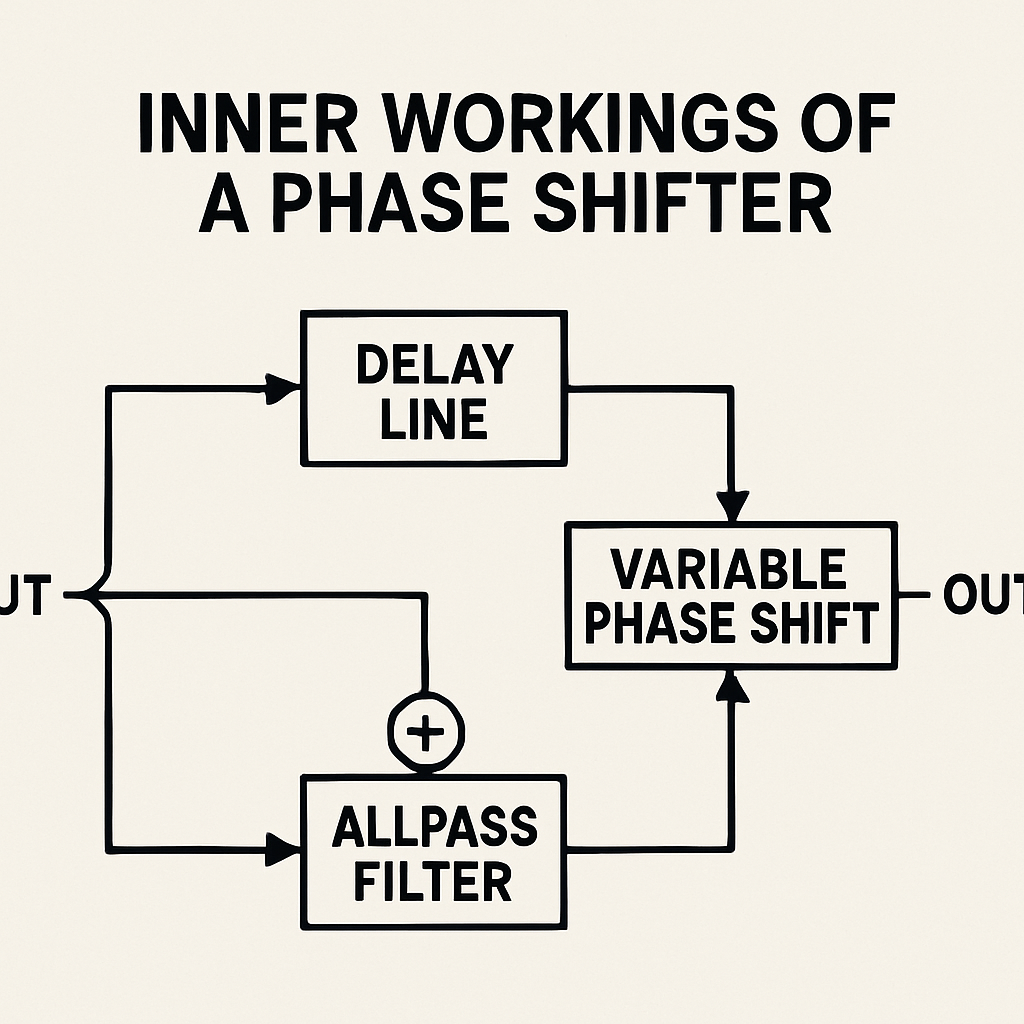
To accomplish this, phase shifters often employ specific techniques:
- Delay lines: Create time delays that adjust the phase.
- Reactive components: Induce phase changes through capacitive or inductive elements.
- Digital processing: Uses algorithms to precisely manage phase shifts.
Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for leveraging phase shifters in technology. Each methodcontributes to the flexibility and precision required in modern electronic systems.
Types of Phase Shifters
Phase shifters vary significantly, depending on their applications and the technologies they employ. The three major types are analog, digital, and RF phase shifters.
Analog phase shifters utilize continuous electrical components like capacitors and inductors. They provide a smooth phase transition.
Digital phase shifters, on the other hand, incorporate digital circuits. They offer precise and rapid phase adjustments.
RF phase shifters are specifically designed for radio frequency applications. These are essential in modulating RF signals effectively.
Each type of phase shifter provides unique benefits, making them suitable for particular technological fields. Here’s a quick overview:
- Analog: Uses reactive components.
- Digital: Leverages software and logic for control.
- RF: Tailored for high-frequency scenarios.
Choosing the right type involves considering factors such as the required frequency range and desired phase precision. Understanding these types aids in selecting the appropriate solution for specific needs.
Analog vs. Digital Phase Shifters
Analog and digital phase shifters serve similar purposes but through different means. Analog phase shifters rely on reactive elements to modify signal phases.
Digital phase shifters, however, use digital control methods. This allows for more precise and programmable phase adjustments.
The contrast between the two is found in their operation and control mechanisms. Analog shifters are generally simpler but less flexible.
Digital phase shifters provide greater precision and adaptability, which is crucial for modern technologies. Consider these factors when comparing:
- Analog:
- Uses continuous variations.
- Typically simpler design.
- Limited flexibility.
- Digital:
- Provides discrete control.
- Highly programmable.
- Ideal for complex applications.
Deciding between analog and digital often depends on the specific needs of the application. Each has its strengths, making them viable in different scenarios.
RF Phase Shifters
RF phase shifters are tailored for applications involving radio frequencies. They are vital in managing the phase of RF signals effectively.
Such phase shifters enable the control of antennas’ radiation patterns. This is crucial in radar and communication systems.
RF phase shifters often employ a variety of designs, including analog and digital technologies. Their versatility makes them indispensable.
When selecting an RF phase shifter, consider factors like frequency range and power handling:
- Types of RF Phase Shifters:
- Switched-line.
- Vector modulator.
- Reflection-type.
The choice of design depends on the specific application requirements. RF phase shifters’ adaptability ensures optimal performance in diverse scenarios.
Digital Phase Shifters
Digital phase shifters offer precise control over signal phases using digital processing. They are essential in complex electronic systems.
These devices allow for programmable phase adjustments, enhancing flexibility and performance. This is particularly advantageous in dynamic environments.
Digital phase shifters can handle various tasks such as beamforming and signal alignment. Their precision is unmatched in comparison to analog types.
These phase shifters are suitable for systems requiring high accuracy and adaptability:
·Advantages:
- Precise and repeatable adjustments.
- Suitable for dynamic changes.
- Integration with digital systems.
The adaptability of digital phase shifters makes them integral in modern technology, supporting advanced communication and processing tasks efficiently.
Maestro Phase Shifters
Maestro phase shifters stand out for their superior performance in demanding applications. They are engineered for high-precision tasks.
These phase shifters are known for handling complex signal processing effectively. They are favored in environments where performance is critical.
Maestro phase shifters are unique due to their robust design and capabilities. Key features include:
- Features:
- High accuracy.
- Superior durability.
- Advanced control mechanisms.
The advanced technology behind maestro phase shifters ensures they meet the rigorous demands of modern applications, enhancing overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Key Characteristics and Performance Metrics
Phase shifters possess critical characteristics that determine their effectiveness in various applications. Understanding these metrics is vital for ensuring optimal performance.
The primary metrics include phase range, resolution, and linearity. Each plays a distinct role in achieving accurate phase adjustments.
Phase range defines the extent to which the phase angle can be altered. A wider phase range offers more flexibility in applications.
Resolution refers to the smallest phase change that can be achieved. High resolution is crucial for precision.
Key performance characteristics often considered are:
- Range: Maximum phase shift capability.
- Resolution: Smallest detectable phase change.
- Linearity: Consistency across the range.
- Insertion Loss: Signal loss introduced.
Linearity is another crucial aspect, ensuring consistent behavior across the entire phase range. Poor linearity can degrade system performance.
Monitoring these metrics helps in selecting the right phase shifter for specific technological applications. Improving these metrics enhances the overall system performance.
Applications of Phase Shifters in Technology
Phase shifters have a pivotal role in advanced technologies. Their applications span diverse fields, making them indispensable.
From telecommunications to radar systems, phase shifters drive innovation. They help improve system efficiency and performance.
In modern communication, they are vital for beam steering and signal quality. They ensure reliable connectivity and reduce interference.
This effectiveness extends into defense technology, enhancing radar precision and secure communications. They’re crucial in electronic warfare systems.
Phase shifters also find use in the medical sector, where image clarity and diagnostics benefit. They contribute to better patient outcomes.
In scientific research, they support experiments involving wave patterns. Their versatility enables a wide range of studies.
Key application areas include:
- Communication Systems: Beamforming, interference reduction.
- Radar Systems: Beam steering, precision targeting.
- Medical Imaging: Enhanced resolution, clarity.
- Scientific Research: Wave pattern studies, diffraction experiments.
- Broadcasting: Signal distribution, quality control
Their use continues to expand with technological advancement, pushing boundaries across sectors.
Phase Shifters in Communication Systems
In communication systems, phase shifters enhance signal integrity and network performance. They are essential in phased array antennas.
Beam steering capabilities allow targeting specific users without moving antennas physically. This enhances network efficiency and reduces interference.
They are critical in 5G networks for massive multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) systems. Phase shifters help direct signals accurately.
Key functions of phase shifters in communication include:
- Beam Steering: Directs signals to desired locations.
- Interference Reduction: Minimizes undesired signal overlap.
- Signal Alignment: Enhances clarity and reduces errors.
- MIMO Optimization: Improves multi-user network operations.
These applications are vital for maintaining seamless connectivity and handling increased data demands.
Phase Shifters in Radar and Defense
Phase shifters are integral in radar and defense systems. They allow for precise control of radar beams, enhancing target detection.
In defense, they ensure secure and effective communication. Phase shifters are used in electronic warfare for signal manipulation.
Their role in radar involves beam steering and target tracking. Phase accuracy is critical for successful radar operations.
Applications in radar and defense include:
- Target Detection: Enhances tracking precision.
- Beam Steering: Adjusts radar beams dynamically.
- Secure Communication: Protects sensitive information.
- Electronic Warfare: Counteracts enemy signals.
Phase shifters improve overall efficiency, ensuring accurate data and security in defense contexts.
Phase Shifters in Medical and Scientific Fields
In medicine, phase shifters enhance imaging technologies. They improve the resolution and clarity of diagnostic images.
They contribute to better medical diagnostics and patient care. This application is critical for non-invasive health assessments.
In scientific research, phase shifters allow for detailed wave interference studies. They aid in understanding complex physical phenomena.
Key uses include:
- Medical Imaging: Enhances image detail.
- Wave Interference: Supports research studies.
- Non-invasive Diagnostics: Improves assessment accuracy.
Their precision makes them invaluable in advancing both scientific and medical technologies.
Phase Shifters in Audio and Broadcasting
Phase shifters influence sound quality in audio systems. They are used to create audio effects, enriching listening experiences.
In broadcasting, they optimize signal distribution and coverage. This ensures consistent audio and visual quality for viewers.
Key applications of phase shifters in this realm include:
- Audio Effects: Enhances sound depth and dynamics.
- Signal Distribution: Optimizes broadcasting coverage.
- Sound Quality: Reduces noise and improves fidelity.
These enhancements transform audio experiences and broadcasting reliability.
Design Considerations and Challenges
Designing phase shifters requires balancing several factors. Engineers must consider size, cost, and performance for optimal functionality.
These devices often face environmental challenges. Temperature variations can affect phase accuracy, necessitating robust design strategies.
Advanced applications demand high-performance metrics, such as low power consumption and fast operation speed. This adds complexity to the design process.
Key considerations include:
- Size Constraints: Minimizing device footprint.
- Cost Efficiency: Keeping production viable.
- Performance Metrics: Ensuring speed and accuracy.
- Environmental Factors: Mitigating temperature impacts.
Overcoming these challenges is crucial for integrating phase shifters into modern technology effectively.
Future Trends in Phase Shifter Technology
Phase shifter technology is evolving rapidly. The demand for efficient, compact systems drives innovation. Future phase shifters will likely focus on miniaturization, enhancing portability and integration.
Technological advancements aim for broader bandwidth capabilities. This is especially crucial in wireless communication and radar systems. Improved bandwidth will lead to more reliable signal processing and better system performance.
Emerging trends also include integration with smart technologies. The adoption of AI and IoT will play a significant role in this integration, enhancing adaptability and performance.
Key future trends include:
- Miniaturization: Reducing size for easier integration.
- Increased Bandwidth: Enhancing signal processing.
- Smart Integration: Utilizing AI and IoT.
These developments promise exciting opportunities for phase shifters across various industries.
Which manufacturer makes good phase accessories
Founded in 2000, Suntop is one of the leading global distributors of electronic components, dedica ted to providing comprehensive procurement and supply chain services to the global electronics manufacturing industry. Our services include distribution, spot trading, PPV cost-saving projects, and inventory management. We not only offer high-quality products but also strive to assist our clients in achieving optimal solutions with minimal time and cost.
As a trusted partner for numerous OEMs, ODMs, CEMs, and EMS companies worldwide, our professional team manages millions of component records from thousands of trading partners across dozens of countries daily through our company database. We maintain close business relationships with major factories and distributors in North America, Europe, and Asia to ensure that our clients stay ahead in a highly competitive market.