why is it called dc gain

by Suntop
2025-09-03
DC gain is a fundamental concept in electronics. It plays a crucial role in amplifier circuits. But why is it called “DC gain“?
Understanding DC gain helps in designing circuits that handle steady signals. It measures how well an amplifier boosts a constant signal. This is vital for applications needing stable output over time.
Voltage amplifiers and current amplifiers both rely on DC gain. It ensures that signals are amplified without distortion. This makes it essential for precision in electronic systems.
DC gain is not just a technical term. It is a key factor in the performance of electronic devices. Knowing its significance can enhance your understanding of electronic circuits.
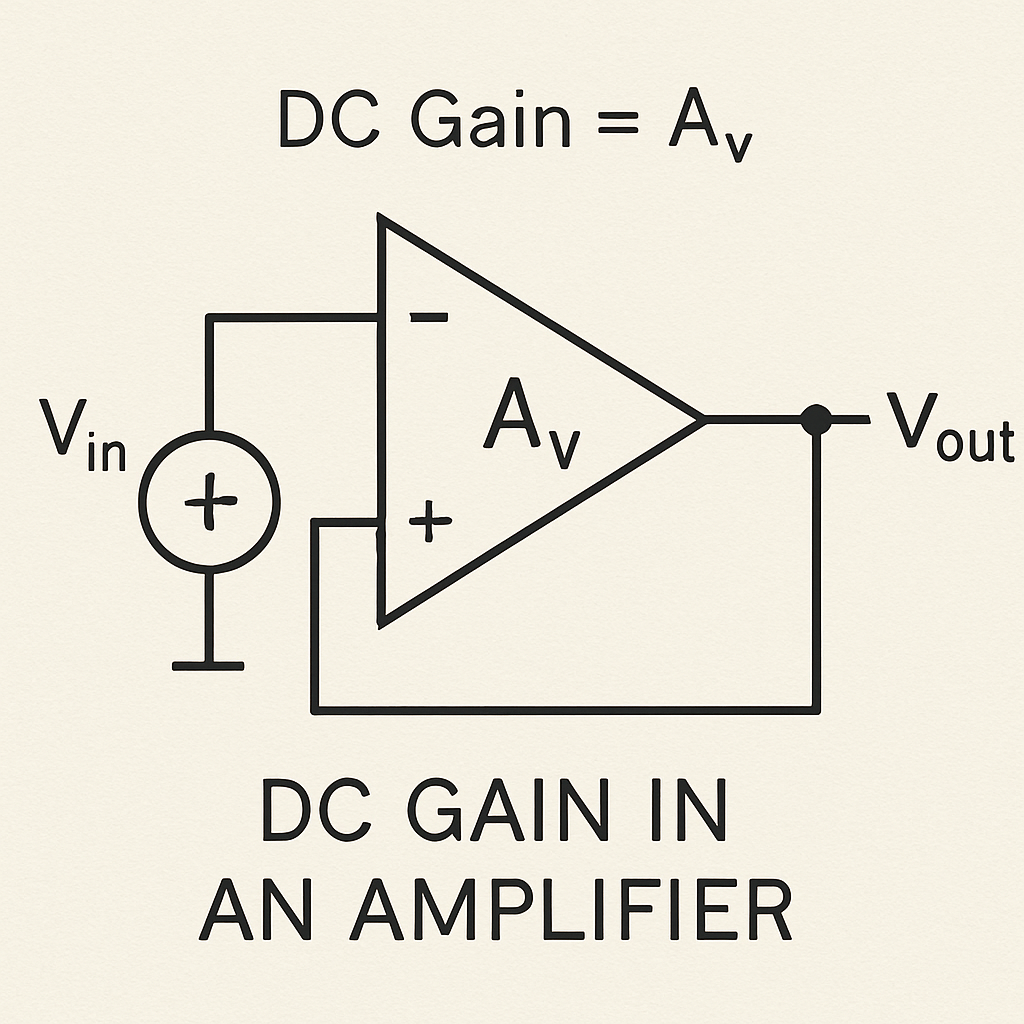
What Is DC Gain? The Basics Explained
DC gain refers to the gain of an amplifier when a direct current (DC) signal is applied. It helps determine how an amplifier deals with steady-state signals. This characteristic is critical for electronic devices that handle constant signals.
In essence, gain is the ratio of the output signal to the input signal. For DC gain, this specifically applies to non-varying (DC) signals. It shows how effectively an amplifier increases the strength of these constant inputs.
DC gain is typically expressed as a dimensionless ratio or in decibels (dB). This makes it easier to compare with other performance metrics. A higher DC gain indicates better signal amplification, which is crucial for many applications.
Key components of DC gain include:
- Voltage amplifiers: Focus on boosting voltage levels.
- Current amplifiers: Target current increases.
- Amplifier circuit diagram: Helps visualize the signal flow and gain.
- Understanding these basics is vital in electronics.
Why Is It Called “DC” Gain?
The term “DC” in DC gain highlights its focus on direct current signals. Direct current signifies a steady, unchanging signal, unlike alternating current which changes direction. Therefore, this type of gain exclusively measures the amplification of constant signals.
This specific terminology is used because it addresses the unique behavior of amplifiers with non-varying signals. DC gain is fundamental in analyzing how stable signals maintain integrity over time. It plays a pivotal role in applications requiring consistency.
Understanding DC gain involves recognizing its core aspects:
- Focus on non-varying signals: Contrasts with alternating signals.
- Stability: Ensures signal integrity over time.
- Specialized function: Distinct from AC gain functions.
The focus on DC gain is not just a technical distinction. It emphasizes its special application in real-world electronics. It remains critical in both learning and advancing electronic technology.
DC Gain in Voltage and Current Amplifiers
DC gain plays a crucial role in both voltage and current amplifiers. A voltage amplifier boosts the input voltage signal’s amplitude. A current amplifier enhances the current of an input signal instead. Understanding DC gain in these contexts can enhance circuit performance.
In a voltage amplifier, DC gain is the ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage. It determines how effectively the amplifier increases the signal. A high DC gain implies a significant increase in signal amplitude.
For current amplifiers, DC gain is the ratio of the output current to the input current. A higher DC gain means better current enhancement. The ratio helps evaluate the amplifier’s ability to drive heavier loads.
Key aspects of DC gain in amplifiers include:
- Voltage amplifier: Focused on amplifying voltage.
- Current amplifier: Concentrated on increasing current.
- High DC gain: Indicates effective amplification.
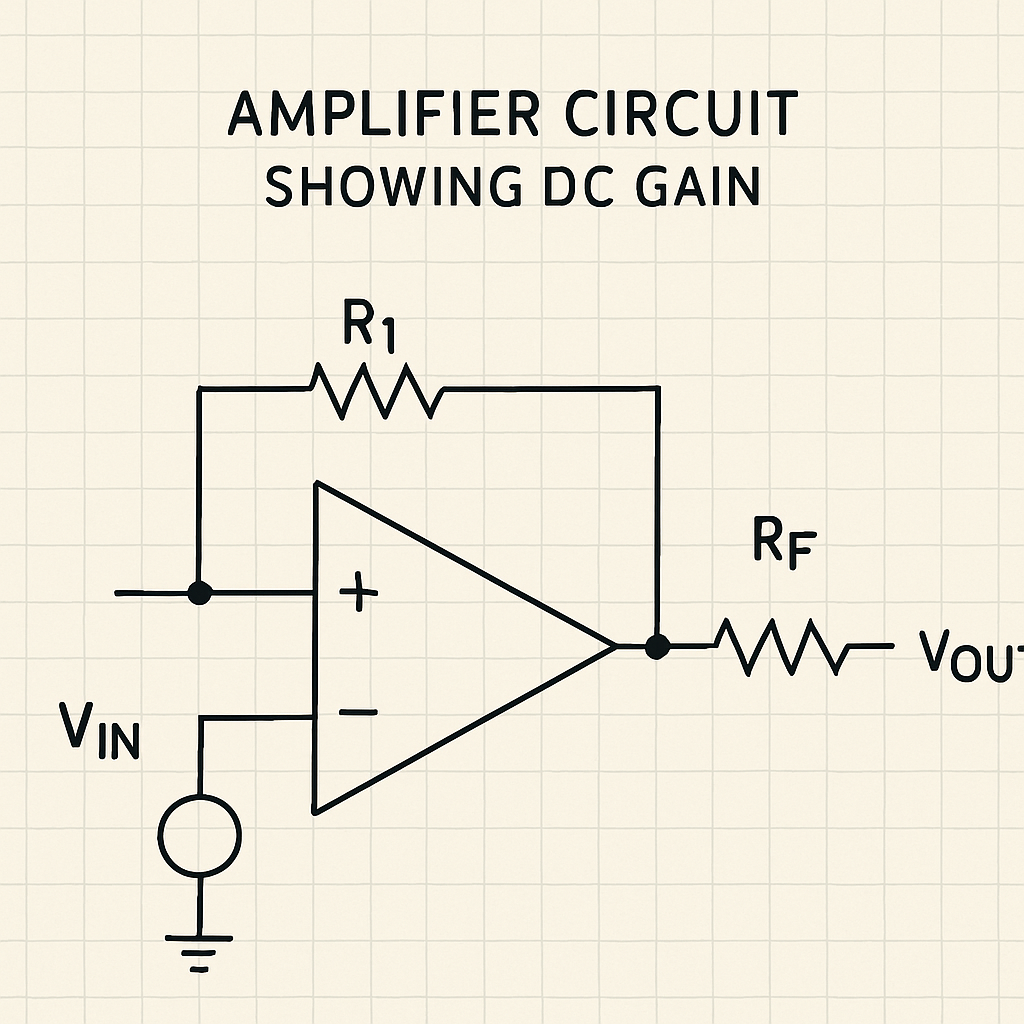
Below is a simplified amplifier circuit diagram illustrating DC gain in action:
Whether boosting voltage or current, DC gain is vital for effective amplification in electronic circuits. It’s essential for design and analysis. Understanding these elements ensures more efficient and reliable circuit designs.
How DC Gain Is Measured and Expressed
DC gain measurement is vital for assessing amplifier performance. It is expressed as a dimensionless ratio. This ratio reflects how much the input signal is amplified. Alternatively, it can be expressed in decibels (dB), which provide a logarithmic scale.
For accurate measurement, a constant voltage source is applied to the input. The output is then observed under these steady-state conditions. This helps identify the amplifier’s efficiency in processing constant signals. Proper tools and methods ensure correct readings.
The expression of DC gain is typically straightforward:
- Ratio: Output signal divided by input signal
- Decibels: (20 \times \log_{10}(\text{Gain Ratio}))
The image below shows a typical setup for measuring DC gain:
These measurements guide designers in optimizing amplifier circuits for various applications. Understanding and accurately determining DC gain leads to better circuit functionality.
DC Gain in Amplifier Circuit Diagrams
Amplifier circuit diagrams are essential for understanding DC gain. They offer a visual representation of the circuit components. These diagrams help in analyzing how an amplifier modifies input signals.
A typical amplifier circuit diagram includes various components. Among them are resistors, capacitors, and transistors. Each part contributes to the overall DC gain performance. Knowing the role of these components can improve design and troubleshooting.
Understanding the diagram helps in identifying potential gain-loss points. Key elements in the diagram are designed to ensure stable DC gain. This stability is crucial for long-term operation of the amplifier.
Common elements in amplifier circuit diagrams include:
- Resistors: Control current flow
- Capacitors: Stabilize voltage changes
- Transistors: Amplify signals
Below is a sample illustration of an amplifier circuit diagram:
Reviewing these diagrams aids in fine-tuning electronic circuits. Adjustments in component values impact the overall DC gain significantly.
The Role of DC Gain in Electronic Circuits
DC gain plays a crucial role in electronic circuits. It ensures steady signal amplification over time. This is vital for maintaining signal integrity in various applications.
Circuits depend on consistent DC gain for stability. This includes audio systems and communication devices. Consistent gain prevents unwanted distortions in the output signal.
DC gain is instrumental in control systems. It ensures that the feedback loop maintains the desired output. This helps in precise control and regulation in automation systems.
Key areas influenced by DC gain include:
- Signal Amplification: Enhances input signals
- Feedback Control: Maintains desired outputs
- Power Efficiency: Optimizes power usage
Visualizing the role of DC gain helps in understanding its impact on electronic performance. Here’s an illustration to clarify its application:
Understanding DC gain helps in designing robust circuits. Engineers can ensure reliable, long-term device performance by managing gain effectively.
DC Gain vs. AC Gain: Key Differences
DC gain and AC gain are fundamental concepts in electronics. They serve different purposes in amplifiers. Understanding their differences is essential for circuit design.
DC gain applies to constant, non-varying signals. It measures the amplifier’s ability to magnify a steady input. This is useful for applications that require signal consistency.
Conversely, AC gain refers to the amplification of alternating signals. It focuses on signals that change over time, such as audio and radio frequencies. AC gain handles the dynamic aspects of signals.
Key differences include:
- Signal Type: DC (steady) vs. AC (varying)
- Application: Stability vs. frequency response
- Impact: Consistency vs. dynamic range
A clear visual can highlight these distinctions further:
Understanding these differences aids in optimizing amplifier performance for specific applications. Whether designing for steady outputs or dynamic signals, both gain types play integral roles in electronics.
Why DC Gain Matters: Applications and Significance
DC gain is crucial in many electronic applications. It ensures the reliable performance of circuits with constant signals. This makes it a cornerstone in designing stable electronic systems.
Many industries rely on DC gain for precise operations. It is vital in audio equipment and communication devices. The stability it provides in amplifiers guarantees consistent signal quality over time.
DC gain also plays an essential role in instrumentation. High precision measurement equipment often depends on amplifiers with optimal DC gain. This ensures accurate readings crucial for scientific and industrial processes.
Applications where DC gain is significant:
- Audio Amplification: Ensures clear sound reproduction.
- Radio Transmission: Maintains signal integrity.
- Instrumentation: Provides reliable data for measurements.
- Control Systems: Supports steady operation.
- Power Supplies: Promotes efficiency and stability.
A visualization can further illustrate these diverse applications:
In summary, DC gain’s role in achieving consistency and precision makes it indispensable in various technological fields. Understanding its importance enables better design choices in electronics.
Factors Affecting DC Gain in Amplifiers
Several factors influence DC gain in amplifiers. Understanding these can improve amplifier design. This leads to more reliable and efficient electronic devices.
One significant factor is temperature. Changes in temperature can alter semiconductor behavior. This affects amplifier performance and stability.
Another factor is component aging. Over time, components can wear out or change properties. This may reduce the DC gain of an amplifier.
Other elements that can impact DC gain include:
- Power Supply Variations: Fluctuations can affect gain consistency.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): External noise can degrade gain stability.
- Component Selection: Quality and type affect overall gain performance.
An illustration of amplifier factors:
By recognizing these factors, designers can take preventive measures. This ensures that amplifiers function optimally under various conditions.
Optimizing and Adjusting DC Gain in Circuit Design
Optimizing DC gain is crucial for effective circuit design. This ensures the amplifier meets desired performance standards. It involves careful selection and arrangement of components.
Adjustments can be made through feedback network design. Feedback loops help control gain levels. They ensure stable and precise amplification.
Common strategies for optimizing DC gain include:
- Component Selection: Choose high-quality resistors and capacitors.
- Circuit Layout: Maintain short paths for signal integrity.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Use feedback loops for control and stability.
By implementing these strategies, engineers can tailor amplifiers to specific applications. This improves both reliability and efficiency in electronic systems.
Common Questions About DC Gain
Many people often have questions about DC gain. Understanding these queries helps in grasping the concept better. Let’s address some common inquiries.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- What is DC gain used for?It is used to measure signal amplification in steady-state conditions.
- Can DC gain change over time?Yes, factors like temperature and component wear can alter it.
- Is DC gain the same in all amplifiers?No, it varies depending on the design and application of the amplifier.
Conclusion
Grasping the concept of DC gain is crucial for anyone working with electronic circuits. It is a key parameter that influences the performance, stability, and reliability of amplifiers.
By understanding DC gain, you can design circuits that deliver stable and efficient performance. This knowledge empowers you to optimize circuits for specific applications, ensuring precise and accurate signal amplification. Mastering DC gain equips you with a vital tool for advancing in electronics and electrical engineering fields.